Mining Coatings — Electroless Nickel NanoDiamond for Severe Abrasion and Corrosion
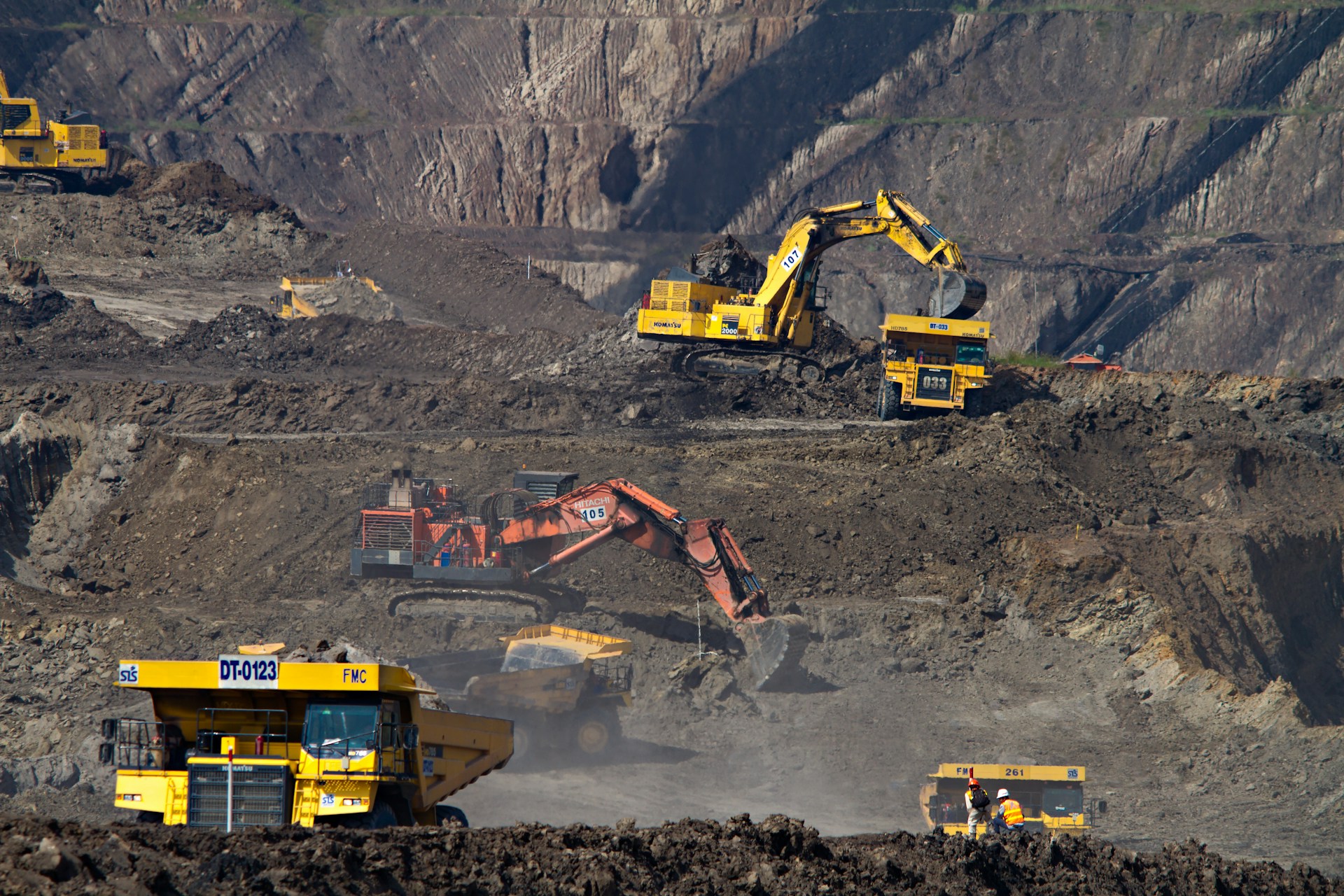
Mining never stops—ore must move, mills must turn, and pumps must run. The problem is relentless triodamage: abrasion from hard particles, erosion from highvelocity slurries, and corrosion from chemically aggressive media. Electroless Nickel NanoDiamond from Metal Diamond is a chromefree, wearresistant, corrosiontough coating engineered specifically for these extreme mining duty cycles—from primary crushing to tailings hydrotransport and beneficiation.
Delivered through a partnerled model (license or joint venture), we enable local coating capacity and supply nanodiamond & electroless chemistries, so mines and OEMs get repeatable quality close to site—with shorter lead times, lower downtime, and better TCO.